The difference between hot and cold forging manufacturing lies in the preproduction stage. If we look at the wording, the idea of hot and cold is actually relative. What it means is when we are forging the springs, the hot forging working temperature is above crystallization; whilst the cold forging temperature is below crystallization. Aside from coiling temperature, there is a difference in the production process as well; the following is a brief explanation for both forging productions.
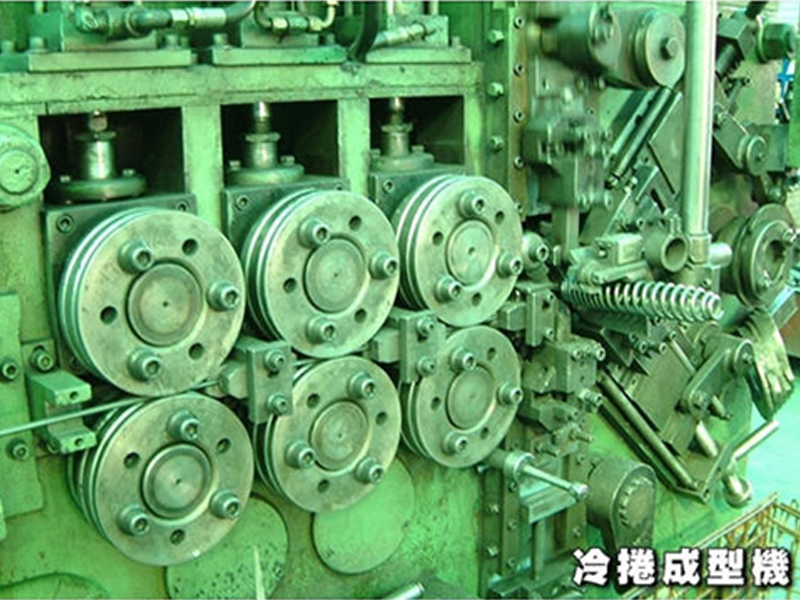
Hot Forging Production Process

Hot forging is often used in the production of larger springs, the process is to first cut of the needed length of the wire, then heating the coil before the coiling process; hence hot forging. Due to the high temperature and the exposure time, it is likely that the product might oxidize or decarburize, which affects the metallic surface structure of the spring, which in turn affects the lifespan and wear and tear tolerance of the spring.
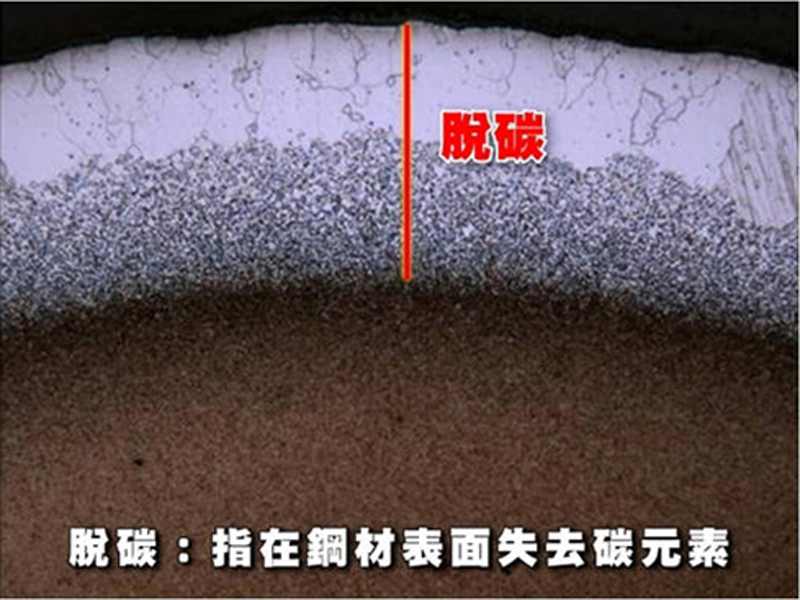
The above photo shows a case of severe decarburization, which will affect the surface quality and even the future processing procedure.
Cold Forging Production Process

Cold forging is usually used on coils with a diameter smaller than 18mm, the procedure is to first heat up the spring steel coil (a strong alloy steel coil), the heating would lead to a solid melting stage for the metallic elements. Then the coil would be quenched, to receive a strong, hard material, which then further gains flexibility through tempering; that's how the coil is treated in cold forging. After these procedures, the material is then put into the forging machine to be coiled into a spring, this would produce a spring with a K value and strength, but the cold forging would lead to a residue of stress, which would affect the size and lifespan of the spring, therefore annealing is applied, to reduce the stress in the spring. Usually, the size of the springs during cold forging would be more precise than hot forging, the quality consistency both on the surface and its internal structure would also be better. However this method cannot be applied to coils with a higher diameter. TS springs use the cold forging method.